The first satellites placed in geostationary orbit were the synchronous communication(SYNCOM)satellites launched by NASA in 1963.
第一个放置在对地静止轨

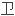 星
星 1963年
1963年

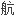 空暨太空总署发射
空暨太空总署发射 同步传输
同步传输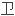 星.
星.
声明:以上例句、词性分类均由互联网资源自动生成,部分未经过人工审核,其表达内容亦不代表本软件的观点;若发现问题,欢迎向我们指正。

 7
7
 集
集 
 5
5
 集
集 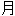 BBC 听力
BBC 听力 
 9
9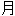
 集
集 These mechanisms would require huge amounts of electricity, which could be provided by solar panels or potentially even nuclear systems. Current designs estimate that it would take about 8 days to elevate an object into geostationary orbit.
这些机制需要大量的电力,这些电力可以由太阳能电池板甚至核系统提供。目前的设计估计,将物体提升到地球静止轨道大约需要 8 天。